Select Seeq Content
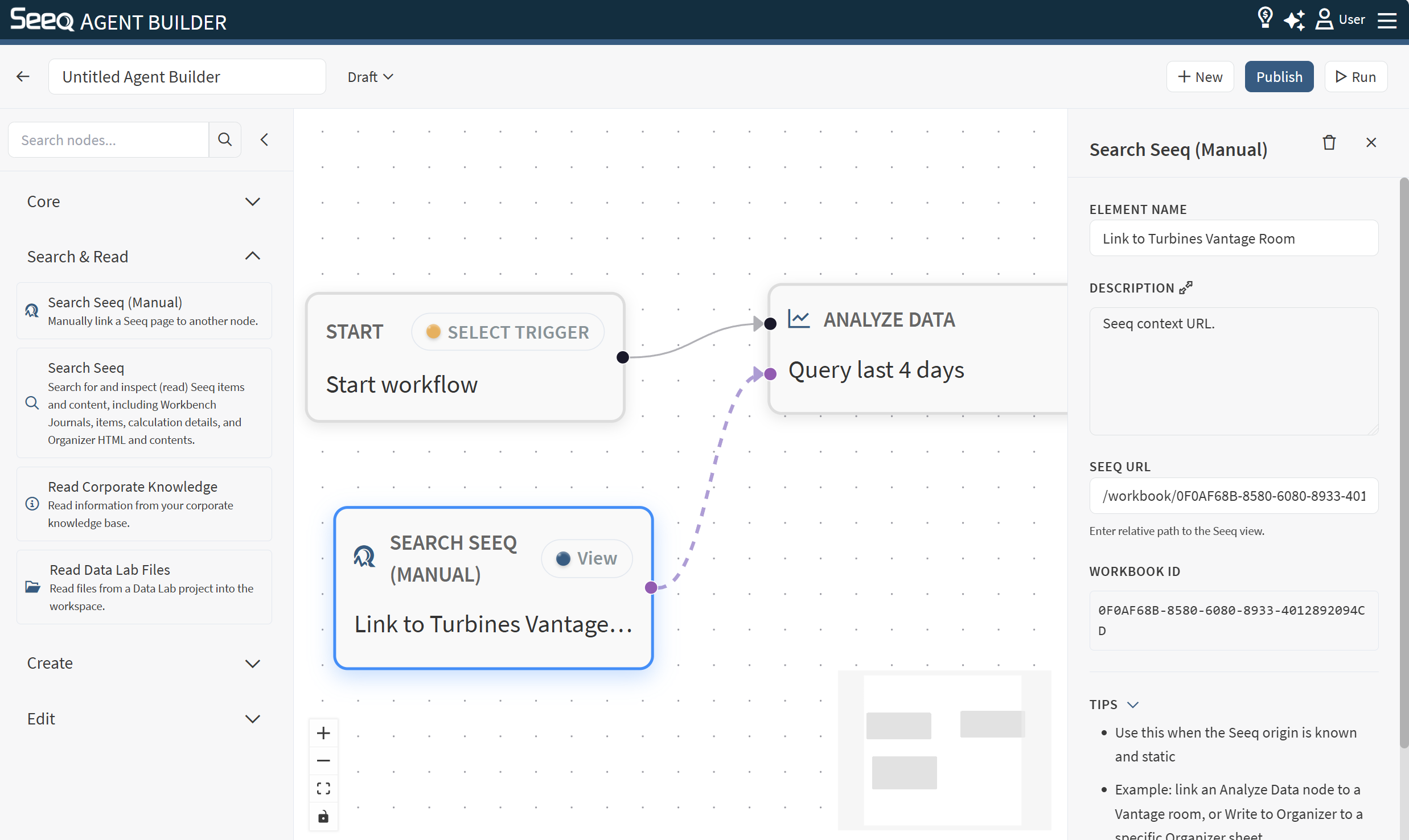
Use Select Seeq Content to associate a workflow with specific content in Seeq—like workbooks, worksheets, folders, Organizer topics/reports, Vantage rooms, and Data Lab projects. This node is most often attached to an Analyze Data node with further instructions of what to do when the Seeq content has been accessed. If you want the workflow to use different content each time it runs based on the prompt, see the Search Seeq node.
When to use
You need to locate a specific workbook/worksheet before reading or analyzing.
You want to find a Data Lab project by name.
You want to reference an Organizer Topic as a template for report generation.
You want links and IDs for Seeq content objects (not items like signals/conditions).
Configuration
Element name: Optional label to make your workflow easier to read.
Instruction: Describe what content to find and what to return. Instructions can be minimal if you are pasting a Seeq URL below the instructions field.
Seeq URL: Optionally paste a URL from anywhere in Seeq.
Using multiple content
You can attach multiple Select Seeq Contents to a node if more than one should be used for the workflow. During execution, the workflow engine can choose an appropriate workbook/worksheet based on:
The current incoming context
The contexts attached to the node
Contexts used earlier in the workflow
Recommendation:
Attach only the contexts you want the workflow to consider; keep the set small and meaningful.
Output
The output typically includes:
The best matching content candidates
Names and relative links
IDs when available (useful for downstream nodes)
Example instructions
Instructions associated with selected Seeq content are written on the Analyze Data node.
“For the linked Vantage Room, pull the last two weeks of events.”
“Read the HTML in the source Organizer Topic.”
Inherited context
Contexts can be inherited from upstream nodes. This makes it easier to attach context once and reuse it downstream.
In the inspector, contexts may appear as:
Direct contexts: Connected directly to this node.
Inherited contexts: Contexts attached to upstream nodes.
