How To: Identify and Remove High Data Lab Disk Usage
Overview
Seeq Data Lab utilizes a file system to store project data such as notebooks, data files, and packages. The Projects tab on the Data Lab Management page includes a “Disk Size” column for reporting the file system usage for a particular project. If the usage is unexpected, or you are looking to reduce the file system usage across Data Lab due to high disk usage warnings, you can investigate a project’s usage to identify any files or folders that can be deleted.
Solution
Open a Data Lab project that you like to investigate high disk usage. Once opened, launch a terminal by clicking the “Terminal” card on the Launcher page, or click File → New → Terminal.
Large Folders and Files
Seeq Data Lab utilizes a Linux OS so any native commands to display disk usage information can be used. Some examples follow:
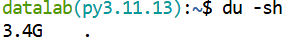
Get the size of the current directory in human readable format (KB, MB, etc):
du -sh
List files in the current directory with human readable file size information (KB, MB, etc):
ls -hl

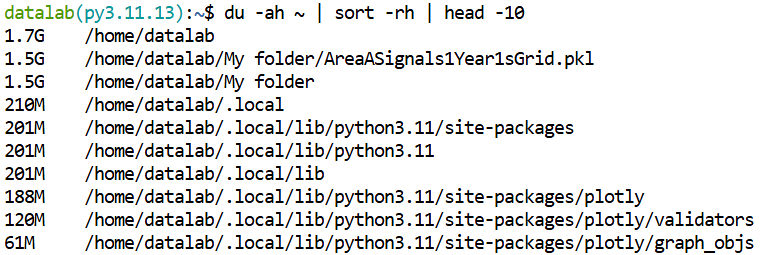
List top 10 largest files and folders in the home directory (~is shorthand for /home/datalab) sorted by size:
du -ah ~ | sort -rh | head -10
Python Packages
A feature of Seeq Data Lab is the ability to install Python packages to your project in any of the supported Python versions. However, some packages can consume a lot of disk space. If none of your notebooks are no longer importing a package, consider removing the package using pip uninstall <pkg> command where <pkg> is the Python package name.
If you would like to check the used disk space for your local packages, run the following command to identify large installed Python packages across all Python versions (including no longer supported versions in Seeq Data Lab).
# Navigate to the .local/lib folder where local Python packages are installed
cd ~/.local/lib
# List top 10 largest folders up to 3 folders deep (to reach site-packages folder)
du -h --max-depth=3 . | sort -rh | head -10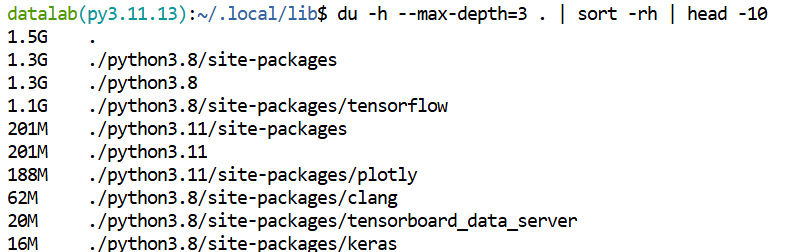
In the example above, the command has identified 1.3GB of disk usage for the /python3.8/site-packages folder and 201MB for the /python3.11/site-packages folder. Specifically tensorflow and plotly are the largest installed. Python packages.
To search a particular local Python package repository, navigate to that directory and execute:
# Navigate to the local Python 3.8 site-packages folder
cd ~/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages
# List top 10 largest child folders sorted by size
du -h --max-depth=1 . | sort -rh | head -10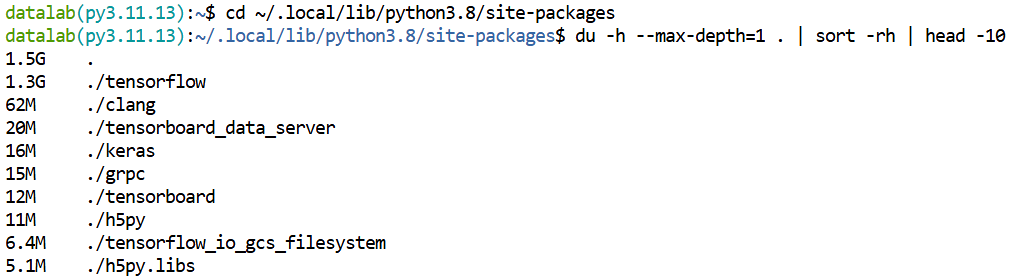
For reference, the path to each local Python package repository is listed below.
Python version | Path |
|---|---|
Python 3.7 (no longer supported) | ~/.local/lib/python3.7/site-packages |
Python 3.8 | ~/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages |
Python 3.11 | ~/.local/lib/python3.11/site-packages |
Trash Folder
When a file or folder is deleted using the JupyterLab interface, the deleted item is moved to a trash folder located at ~/.local/share/Trash. The trash folder acts as a recycle bin by persisting the item for a potential restore. Folders and files removed from the Data Lab terminal are not moved to the Trash folder, but are permanently deleted.
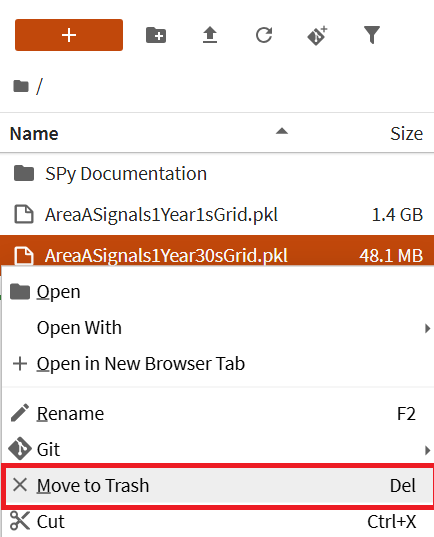
Move an item to Trash
After 30 days, the trashed items will be permanently deleted automatically. Therefore, trashed items deleted less than 30 days ago still consume Data Lab disk usage. You can view and remove these items manually through the terminal.
cd ~/.local/share/Trash/files/
ls -al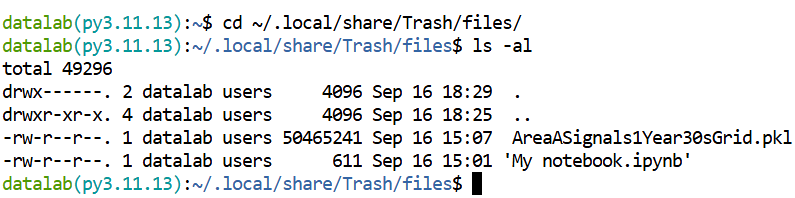
The Trash folder items
You can permanently delete the item or restore it by moving it to the desired location.
# Restore My notebook.ipynb to root folder (~)
mv 'My notebook.ipynb' ~
# Permanently delete AreaASignals1Year30sGrid.pkl
rm AreaASignals1Year30sGrid.pkl 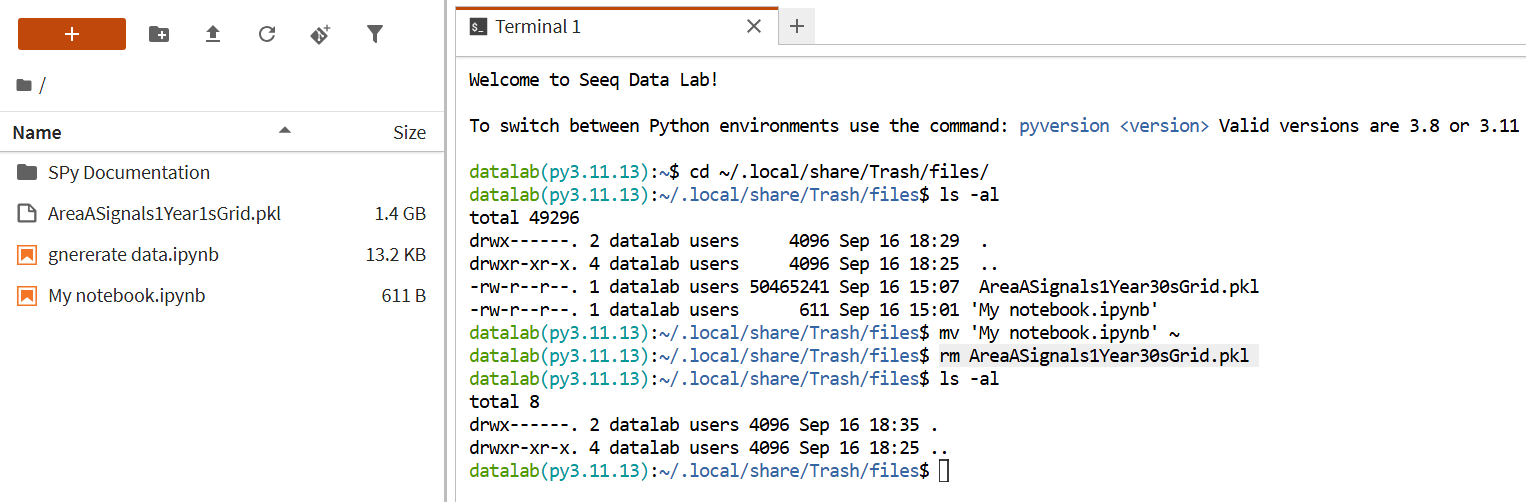
Restored and Deleted Trash item
Cache Folder
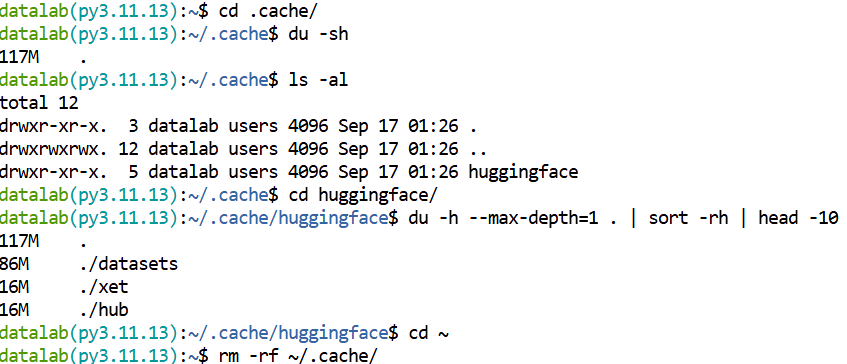
Some Python packages may load external data (such as datasets) or store runtime data in the ~/.cache folder, which is a hidden folder since it start with a dot. If the cache folder is large and no longer necessary consider removing its contents or the directory in entirety.
Global Python Packages
Seeq Data Lab allows admins to install Python packages across all projects to eliminate the need from repeated installations in multiple projects, particularly for long installation times or large packages. Much in the same way local Python packages can be investigated, so too can global Python packages.
# Navigate to the global Python 3.11 site-packages folder
cd /seeq/python/global-packages/lib/python3.11/site-packages
# List top 10 largest child folders sorted by size
du -h --max-depth=1 . | sort -rh | head -10
For reference, the path to each global Python package repository is listed below.
Python version | Path |
|---|---|
Python 3.8 | /seeq/python/global-packages/lib/python3.8/site-packages |
Python 3.11 | /seeq/python/global-packages/lib/python3.11/site-packages |
